VA Home Loans Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need a down payment for a VA loan?
VA loans don’t require any down payment. In fact, VA home loans However, you may find that you can get a lower monthly payment by putting a down payment on your VA loan. Whether or not you choose to make a down payment on a VA mortgage loan is up to you.
What’s the most I can borrow with a VA home loan?
VA loan county loan limits are the basis of allowable loan amounts in the U.S. In the majority of U.S. counties in 2014, the loan limits on VA loans is $417,000.
This means that the maximum amount that can be financed with a VA loan is $417,000. If the home you wish to purchase or refinance with a VA loan has a market value above the loan limit, you can either put a down payment on the loan that is large enough to cover the remaining home value amount or apply for an exception, which may be granted in some cases.
The Department of Veterans Affairs sets a list of counties that allow for higher loan limits due to the standard cost of housing and living within higher cost counties in every state. (For example, the loan limit in most Alaskan counties is $625,000 because the average home price and cost of living is higher than the national average.)
The loan limits—or guaranty amounts—that go above and beyond the national standard are revised annually by the VA. You’ll be advised of the loan limits in your county when you speak to a VA Loan Specialist.
Can I have multiple VA loans out at once?
It’s rare that a veteran will be able to take out more than one VA mortgage loan at one time, but there are circumstances that would permit it.
Can I use a VA loan to purchase a rental property or a business?
No. VA loans can only be used to finance primary residences. It is possible, however, to refinance a property that you used to reside in but currently rent out. However, in terms of purchasing, VA loans can only be used to homes in which you intend to live.
Can I use my VA loan benefit more than one time?
Yes. VA home loans can be used again and again, so long as you satisfy the requirements of VA loan entitlement.
Are VA mortgage loans complicated?
VA loans aren’t usually complicated to the borrower. While they do require a bit more paperwork than some other loan types, the loans themselves are pretty consumer friendly. In fact, VA IRRRLs—or refinance loans that are designed to lower the interest rate on an existing VA loan—require very little paperwork and are usually processed very quickly.
How long does it take to get a VA loan?
This is entirely dependent on the nature of your VA loan. VA to VA refinancing can take less than 30 days to close the loan. Purchasing may take a bit longer. On average, a VA loan closes somewhere between 45 days and 90 days after you apply.
Can I get cash back when I get VA refinance loans?
Yes—you can get up to 100% equity cash out on VA loans here at NLC Loans. However, no cash out options are available for VA IRRRL loans—or VA to VA refinancing loans. IRRRLs are simply designed to reduce interest rate on an existing VA loan.
How can I get pre-approved for VA loans?
In order to get pre-approved for a VA loan, you need to contact a VA Loan Specialist here at NLC Loans.
You’ll be required to submit certain documents, such as a Certificate of Entitlement, proof of income, and undergo a credit check. However, if you’re just looking to lower your interest rate on a current VA loan, you can refinance with little paperwork and no eligibility or income verification.
What are the benefits of a VA loan?
In general, VA loans save homebuyers and homeowners more on average than any other loan type.
VA loans at NLC loans qualify for 100% equity cash out refinancing in many cases, have lower interest rates and monthly payments, require no down payment, have no mortgage insurance premiums attached to them and are the best option from a financial standpoint for most eligible veterans who are looking to buy or refinance a home.
What fees are associated with VA home loans?
The VA sets a maximum amount that borrowers have to pay in terms of fees when they obtain a VA loan. This is helpful to our clients because it allows them to save money in terms of fees on VA loans.
A 1% loan origination fee and 1% administrative fee are usually charged on a VA loan. Closing and concessions costs—which can cost up to 6% of the loan amount—are often paid by sellers and not borrowers.
A VA funding fee is also charged, which is unique to each VA loan. This is the cost the VA loan program charges to keep the VA loan program afloat. This fee also helps other veterans take advantage of VA home loans.
Can I get fixed or adjustable rate VA loans?
Yes—you can get either a VA ARM loan or a fixed-rate VA home loan. Both types are offered.
What’s the minimum credit score to get a VA loan?
In general, the minimum credit score required to get a VA loan is 580. However, there are other credit considerations as well.
Can I get VA loans with bad credit?
You do not need to have perfect credit to obtain a VA home loan. VA loans have less stringent credit requirements than do conventional home loans. In general, a credit score minimum of 580 is a golden standard. Other items—such as income, presence of a bankruptcy or foreclosure, open collections accounts, or being more than 30 days late on a recent mortgage loan will be considered on your VA home loan application.
Our loan specialists will be able to look at your credit and let you know what you might need to address at the time you apply with us. In general, however, imperfect credit will not bar you from getting a VA loan as a whole.
Can I get a cosigner or co-applicant on a VA loan?
Yes, but the person cosigning or co-borrowing alongside you must either A. be your spouse or B. be another VA loan-eligible veteran. Other friends or family members who do not fall into one of those two categories cannot be listed as a cosigner or co-borrower on a VA home loan.
Can I get a VA loan after bankruptcy or a foreclosure?
As a general rule, two years must have elapsed since your bankruptcy discharge or foreclosure. This doesn’t mean that you will automatically qualify after this time period, but it usually means that it won’t automatically bar your from VA home financing.
What type of income is accepted on a VA loan application?
In general, two years of stable income is required to be approved for a VA loan. Approved income sources include military pay and allowances, other employment, self-employment, spousal employment, commissions, rental property income, retirement income, alimony and child support.
What is entitlement?
Entitlement is a guaranteed amount of financing from the Department of Veterans Affairs that every service member and veteran who meets basic eligibility requirements for home purchase or refinance with a VA loan.
Entitlement can be looked at as an insurance policy up to a certain amount that guarantees a VA approved lender that you will repay your VA loan as agreed. It’s similar to private mortgage insurance, but you don’t pay for it—the VA does.
Once you’ve paid off a VA loan or sold the property that you financed with it, your entitlement can be restored and you can be eligible for another VA loan.
Where can I get my Certificate of Eligibility (COE)?
This document is available from the Department of Veterans Affairs. When you speak to a VA loan specialist here at NLC Loans, they’ll be able to access your COE or tell you how to obtain it easily.
Do I need to get an appraisal for a VA home loan?
If you are purchasing a home or taking cash out on a VA refinance, you will likely need to obtain an appraisal at your own cost to process your loan. If you are simply attempting to lower your interest rate on an existing VA loan (VA to VA or IRRRL), you probably won’t need an appraisal.
Are you eligible for a VA Loan?
Both active military members and veterans can be eligible for VA home loan financing. VA loan qualifications vary depending on the wartime and/or peacetime period served or current service length. Reserves and National Guard members may also be eligible. In order to obtain the document needed to prove eligibility—the Certificate of Eligibility (COE)—military members and veterans must meet some basic VA home loans eligibility guidelines.
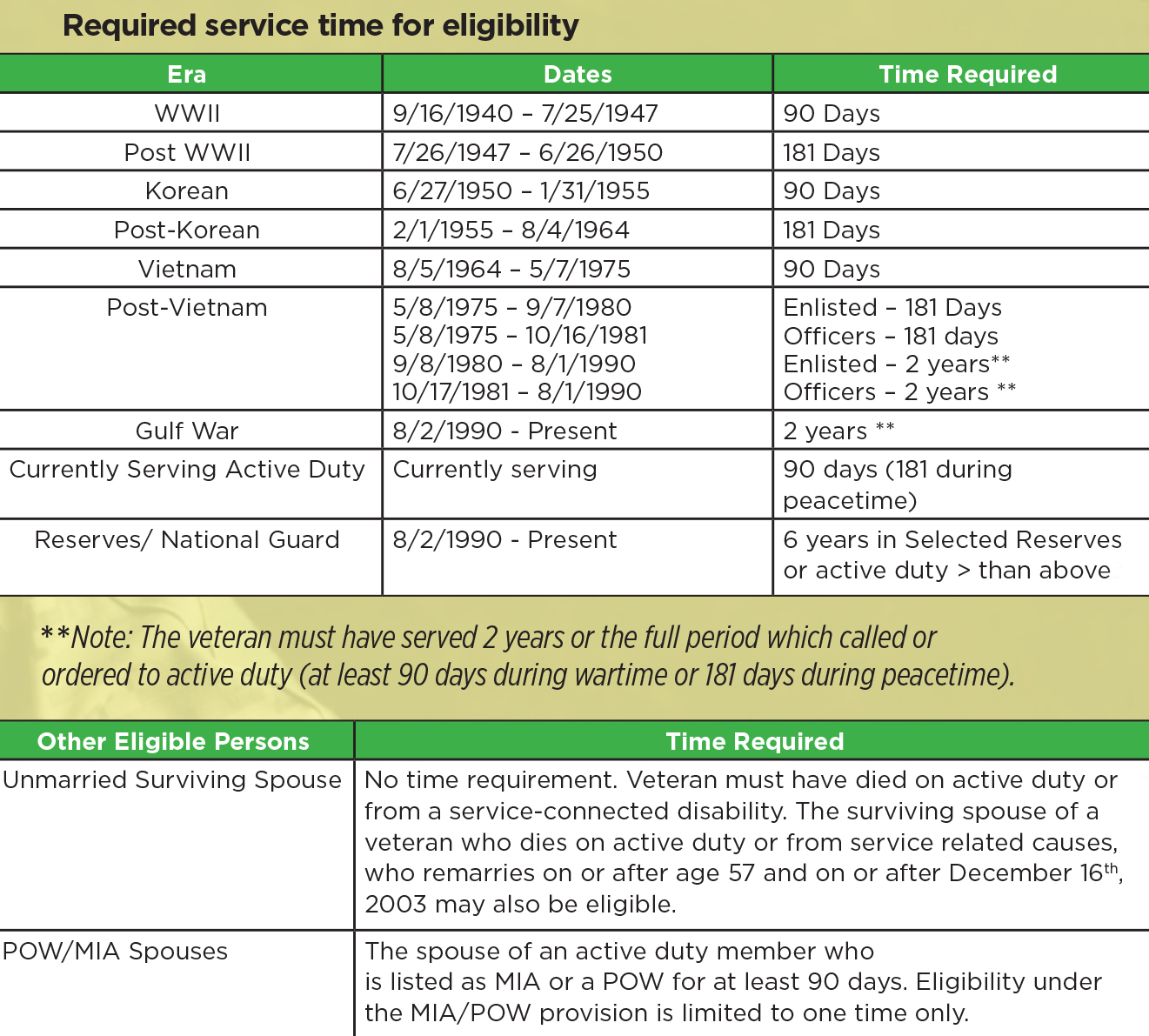
Other VA Home Loans Eligibility Guidelines
There are other instances in which one might be eligible to get a VA loan. For example, if you were a military member and were discharged due to certain medical conditions, a service-related injury, a reduction in force, hardship, or for government convenience, you may still be able to obtain a Certificate of Eligibility so that you can buy or refinance a home with a VA loan.
Military Spouses and VA Loan Eligibility
The spouses of eligible veterans may also be eligible to get VA loans. In order to qualify, a spouse must meet some very specific requirements:
- Spouse must have been married to an eligible veteran who died in service or of a service-related injury or disability.
- VA eligible spouse must not be remarried. However, there are certain rules that do allow VA loan eligibility if the surviving spouse marries after age 57 in some cases.
- Spouse of an active military member who is listed as MIA or POW
- Surviving spouses of specific veterans who were completely disabled due to a service related injury before they passed away, even if the death was not a direct result of the service related injury
Less Common VA Home Loan Eligibility Circumstances
In addition to veterans and active service members, certain other people may be eligible to get VA home loans as well. These include:
- U.S. citizens who served the militaries of other countries that were U.S. Allies during WWII
- Current or past service members who are or were midshipmen at the U.S. Naval Academy
- Current or past NOAA officers
- Current or past merchant seamen who served in World War II
- Current or past Public Health Service Officers
- Current or past cadets of the U.S. military, Coast Guard or Air Force
What is VA Loan Entitlement?
Entitlement is the official word the Department of Veterans Affairs uses to describe VA loan funding availability for eligible veterans. Eligible veterans can only receive one VA loan at a time, so if the home financed on by their first VA loan is foreclosed on or goes unpaid, their entitlement gets “used up.”
In general, entitlement can restored once a veteran pays off or sells his or her home. However, another veteran may assume the loan of another. This can occur when another eligible veteran agrees to have the VA home loan transferred to them and use their own entitlement so that the selling veteran’s entitlement can be restored.
Additionally, entitlement can be restored of the veteran has paid off the VA home loan so long as he or she has not gotten rid of the property that had been paid off with a VA loan.





 newsletter no longer available
newsletter no longer available